Tooth pain often comes suddenly, and the discomfort can be so intense that most people look for the fastest relief. Many ask, “What is better for tooth pain, Tylenol or Ibuprofen (Advil)?” Both work well for dental pain, but each handles pain differently. Knowing how they work helps you choose the right one for the type of toothache you are experiencing.
Both medications are easy to find and generally safe, but the choice depends on the cause of your pain. Here is a clear explanation to help you make the right decision.
How Do Advil and Tylenol Work for Tooth Pain?
Before choosing a pain reliever, you should understand what type of discomfort you have. Most dental pain involves inflammation, especially when it comes from cavities, infections, gum irritation, or a cracked tooth. Ibuprofen targets inflammation, which makes it very effective for these conditions. It works by reducing the inflammatory response around the tooth and nearby tissues.
Many people also ask, “Will Tylenol (Acetaminophen) help with a toothache?” Yes, it can. Tylenol works by blocking pain signals in the brain, so you feel less discomfort. It helps with general pain but does not target swelling. This makes it useful when inflammation is not the main issue.
Which Tooth Pain Responds Best to Advil vs Tylenol
Different types of tooth pain respond to medication in different ways. Understanding the source of the pain helps you choose the right option. Most dental discomfort happens because the tissues around the tooth are swollen or irritated. In these situations, Advil offers stronger relief because it calms the inflammation that creates pressure and throbbing.
Tylenol works better when the pain is not linked to swelling. It helps with mild nerve irritation, headaches that come with tooth pain, and discomfort that feels dull instead of sharp. People with sinus-related tooth pressure, sensitivity to temperature changes, or general soreness may feel better with Acetaminophen because it reduces how the brain perceives pain.
Pain from infections, gum swelling, or a cracked tooth usually responds more to Ibuprofen because these issues involve inflammation. Post-extraction pain also improves more with NSAIDs, especially during the first two days while the tissues are healing. If inflammation is the main problem, Advil generally brings clearer and faster relief.
Which One Works Faster for Tooth Pain?
For most dental problems, Ibuprofen tends to work faster because it reduces swelling, which is the main cause of sharp or throbbing pain. If you have intense discomfort and want quick relief, Advil usually helps within 20 to 30 minutes as the inflammation settles.
Tylenol offers relief too, but it takes longer to work and does not address inflammation. It helps decrease pain perception, but it will not calm irritated or swollen tissues. Even so, it remains a safe and effective option for people who cannot take NSAIDs.
Can You Combine Advil and Tylenol for Tooth Pain?
Many dentists recommend combining Ibuprofen and Acetaminophen for stronger relief when the pain is intense. Each medication works in a different way, so using them together offers broader control. Ibuprofen reduces swelling around the tooth, while Tylenol blocks pain signals. The combination helps when one medication alone is not enough.
This approach often works well for severe dental pain, including infections, impacted teeth, and early post-extraction discomfort. Alternating the two on a schedule keeps the relief steady and prevents sudden spikes in pain. It is important to follow safe dosage limits and avoid taking more than the recommended amount.
Combination therapy should only be used if you do not have medical conditions that restrict either medication. People with liver disease should not take high doses of Tylenol, and those with kidney problems or stomach ulcers should avoid NSAIDs. If you are unsure about the right dose or timing, a dentist or physician can guide you.
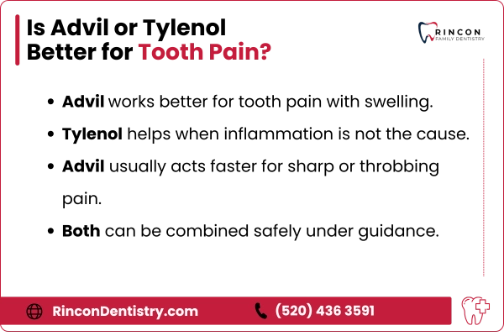
When Should You Choose Tylenol vs. Advil?
Choosing between the two depends on the source of the pain. If your tooth is cracked, infected, or causing gum irritation, Ibuprofen is usually the better choice. It controls both the swelling and the discomfort, which brings stronger overall relief.
Tylenol remains a good option when inflammation is not the main problem or when you cannot take Ibuprofen. It is often recommended for individuals who are allergic to NSAIDs, pregnant, or have stomach ulcers, gastrointestinal bleeding disorders, or medical conditions that affect the heart, kidneys, or liver. In these cases, Acetaminophen offers safe and consistent relief when used at the correct dosage.
Some people also combine both medications in alternating intervals under professional guidance. This provides stronger relief because each works differently in the body. However, you should never combine them without checking dosage limits or confirming it with a dentist or physician.
Safety Warnings: Who Should Avoid Each Medication
Although Advil and Tylenol are widely used, not everyone can take them safely. Understanding the risks helps you choose the right option without causing further problems. Ibuprofen is not suitable for people with stomach ulcers, kidney disease, bleeding disorders, heart conditions, or known allergies to NSAIDs. It can irritate the stomach lining and affect kidney function, so people with these issues must avoid it.
Tylenol is processed through the liver, so it should not be used by individuals with liver disease, heavy alcohol use, or a history of liver damage. Exceeding the daily limit is unsafe, even when the pain is severe. Pregnant individuals are usually advised to choose Tylenol, but dosage should always be confirmed with a doctor.
If you take prescription medications, have chronic medical conditions, or are unsure how much to take, consult your dentist or physician before using either option. This ensures that the pain relief you choose is both effective and safe based on your health needs.
When to See a Dentist
Advil and Tylenol only reduce the discomfort. They do not treat the actual cause of the toothache. If your pain lasts longer than 24 to 48 hours or you notice symptoms such as fever, swelling, difficulty chewing, or a bad taste in the mouth, you should see a dentist right away.
Pain relievers cannot treat infections, nerve inflammation, or deeper dental problems. They are meant to manage discomfort for a short time until you receive proper treatment. Only a dentist can identify the source of the pain and provide long-term relief.
Conclusion
Both Advil and Acetaminophen help with tooth pain, but Ibuprofen usually provides faster and stronger relief because it targets inflammation. Tylenol is still a dependable choice for people who cannot take Ibuprofen or need general pain control. The better option depends on your health conditions and the type of toothache you are dealing with. If your symptoms continue, a dental visit is necessary to find the true cause and treat it properly.
Also Read:
- How to Reduce Tooth Pain After a Filling
- Signs of Needing a Root Canal
- Why Would I Need a Root Canal?
FAQs
How do you stop a throbbing nerve pain in your tooth?
Ibuprofen or Tylenol, cold compresses, a lukewarm saltwater rinse, and clove oil may help reduce discomfort, but long-lasting relief requires a dental evaluation.
What is the best painkiller for a toothache?
Ibuprofen (Advil) is often the most effective because it reduces both pain and inflammation. A dentist may also recommend combining it with Tylenol at safe intervals.
Is it safe to take Tylenol for a toothache while pregnant?
Yes. Tylenol is considered safe during pregnancy, but you should always confirm the correct dosage with your doctor.
Can I take Advil after a tooth extraction?
Yes, you can take it if your dentist recommends it and you do not have allergies or medical conditions that prevent NSAID use.